Creatinine 2.7 : Is it Dangerous, Causes, Symptoms and More
When it comes to understanding our health, it's crucial to pay attention to the numbers that appear in our medical reports. One such number is the creatinine level, an indicator of kidney function. If your creatinine level is at 2.7, it's essential to understand what this might mean for your overall health. Elevated creatinine levels can signal potential kidney issues, which could be dangerous if left unaddressed. In this blog, we will delve into the causes behind high creatinine levels, the symptoms you should watch out for, and the treatments available to manage this condition effectively.

What is Creatinine
Creatinine is a byproduct of protein breakdown and serves as a waste product that the body needs to eliminate. It is produced by muscles during normal wear and tear and is filtered out of the blood by the kidneys. Since creatinine has no use in the body, its levels in the blood can indicate how well the kidneys are functioning. Elevated creatinine levels can signal potential kidney issues, making it crucial to monitor and address any significant changes.
- Muscle Metabolism: Creatinine is a byproduct of the normal breakdown of muscle tissue.
- Meat Consumption: Diets rich in red meat can contribute to higher levels of creatinine.
- Kidney Function: The kidneys filter creatinine out of the blood, so impaired kidney function can lead to higher levels.
- Exercise: Intense physical activity can temporarily elevate creatinine levels due to increased muscle breakdown.
- Medications: Certain drugs, such as antibiotics and NSAIDs, can affect kidney function and creatinine levels.
- Dehydration: Insufficient fluid intake can concentrate creatinine levels in the blood.
- Creatine Supplements: Supplements used by athletes to enhance performance can convert to creatinine.
Normal Range of Creatinine in Adults
In adults, the normal range of creatinine levels in the blood typically falls between 0.6 to 1.2 milligrams per deciliter (mg/dL) for men and 0.5 to 1.1 mg/dL for women. These values can vary slightly depending on the laboratory and the methods used for testing. Creatinine levels are a critical indicator of kidney function, as kidneys are responsible for filtering creatinine out of the blood. Elevated creatinine levels can signal potential kidney issues, making it essential to understand what constitutes a normal range.
| Age Group | Normal Creatinine Range (mg/dL) |
|---|---|
| Infants (up to 1 year) | 0.2 - 0.5 |
| Children (1-12 years) | 0.3 - 0.7 |
| Adolescents (13-18 years) | 0.5 - 1.0 |
| Adults (Male) | 0.6 - 1.2 |
| Adults (Female) | 0.5 - 1.1 |
| Older Adults (60+ years) | 0.6 - 1.3 |
Causes of Creatinine 2.7
Elevated creatinine levels can be a cause for concern, as they often indicate potential issues with kidney function. There are several factors that can lead to an increase in creatinine, ranging from chronic kidney disease and acute kidney injury to conditions like dehydration and muscle disorders. Understanding the underlying causes is crucial for determining the appropriate treatment and managing overall health effectively.
- Dehydration: Lack of sufficient fluids can lead to high creatinine levels.
- Kidney Disease: Conditions such as chronic kidney disease can impair kidney function, leading to elevated creatinine.
- High Protein Diet: Consuming a diet rich in protein can temporarily increase creatinine levels.
- Medications: Certain drugs, like nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), can affect kidney function.
- Intense Exercise: Vigorous physical activity can cause a temporary rise in creatinine due to muscle breakdown.
- Diabetes: Poorly managed diabetes can lead to kidney damage, resulting in elevated creatinine.
- Hypertension: High blood pressure can damage the kidneys over time, increasing creatinine levels.
- Infections: Severe infections can impact kidney function, leading to higher creatinine readings.

Symptoms of Creatinine 2.7
Elevated creatinine levels can be a significant indicator of underlying health issues, particularly related to kidney function. When creatinine levels rise above the normal range, it may suggest that the kidneys are not effectively filtering waste from the blood. Common symptoms of elevated creatinine include fatigue, swelling or edema, changes in urine output, and shortness of breath. Recognizing these symptoms early can be crucial for timely diagnosis and treatment, ultimately helping to prevent further complications.
- Fatigue: Persistent tiredness and lack of energy.
- Swelling: Noticeable swelling in the face, ankles, or hands.
- Shortness of Breath: Difficulty in breathing or catching your breath.
- Confusion: Mental fog, confusion, or trouble concentrating.
- Muscle Cramps: Frequent muscle cramps or spasms, especially at night.
- Changes in Urine: Noticeable changes in the frequency, color, or consistency of urine.
- Nausea: Feeling nauseous or vomiting without a clear cause.
- High Blood Pressure: Elevated blood pressure levels that are difficult to control.
Dangers of Creatinine 2.7
Understanding the implications of elevated creatinine levels is crucial for maintaining overall health. While creatinine itself does not directly harm the body, its elevated levels are often a significant marker of underlying health issues, particularly concerning kidney function. When the kidneys are not functioning correctly, they fail to effectively filter out waste products, leading to an accumulation of substances like creatinine in the blood. This condition can be a warning sign of kidney failure or other serious health problems. Additionally, other waste products like urea can build up in the body and cause harmful effects, further emphasizing the importance of addressing the root causes of elevated creatinine levels promptly.
- Kidneys: Elevated creatinine levels are a primary indicator of kidney dysfunction or chronic kidney disease, leading to reduced ability to filter waste from the blood.
- Heart: High creatinine can be associated with an increased risk of cardiovascular diseases, including heart attack and stroke.
- Liver: Although less common, it can indicate severe liver disease, which may impact the liver's ability to metabolize creatinine.
- Muscles: Elevated levels might point to muscle damage or disorders such as rhabdomyolysis, where muscle fibers break down and release creatinine into the bloodstream.
- Lungs: Kidney disease linked with high creatinine can lead to fluid accumulation in the lungs, causing breathing difficulties.
- Brain: High creatinine levels can cause neurological symptoms like confusion, fatigue, and difficulty concentrating, indicative of uremic encephalopathy.
- Skin: Chronic kidney disease might lead to skin changes such as dryness, itchiness, and pallor due to toxins building up in the body.
- Digestive System: Elevated creatinine can result in gastrointestinal issues like nausea, vomiting, and loss of appetite, affecting overall health and nutrition.
Home remedies for Creatinine 2.7
Disclaimer: Elevated creatinine levels cannot be effectively treated at home and require professional medical attention. If you or someone you know has a creatinine level of 2.7, it is crucial to consult a healthcare provider for a proper diagnosis and treatment plan. Basic supportive care includes staying well-hydrated, following a renal-friendly diet low in sodium, potassium, and phosphorus, and avoiding over-the-counter medications that can further strain the kidneys. However, these measures are not substitutes for professional medical treatment and should only be considered as part of a comprehensive care plan under a doctor's supervision.
- Stay Hydrated: Drinking plenty of water can help your kidneys function more effectively and reduce creatinine levels.
- Monitor Protein Intake: Reducing the amount of protein you consume can lessen the burden on your kidneys. Opt for plant-based proteins where possible.
- Avoid Over-the-Counter Pain Medications: Some pain relievers like ibuprofen and aspirin can harm your kidneys, so it's best to avoid them unless prescribed by your doctor.
- Maintain a Balanced Diet: Eating a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains can support overall kidney health and potentially lower creatinine levels.
- Exercise Regularly: Engaging in moderate physical activity can improve your general health and support kidney function. However, avoid strenuous exercise as it can increase creatinine levels temporarily.
Treatment for Creatinine 2.7
When creatinine levels reach 2.7, medical treatment by a doctor is required to address potential underlying causes and prevent further complications. The primary treatment goals include stabilizing kidney function, which may involve dietary changes, medications, and monitoring fluid intake. It is also crucial to stop any harmful drugs that could be contributing to kidney damage. Additionally, if infections are present, treating infections promptly with appropriate antibiotics or antiviral medications can help in reducing the strain on the kidneys and improving overall health outcomes.
- Hydration: Increasing fluid intake can help dilute creatinine levels in the blood and support kidney function.
- Dietary Changes: Reducing protein intake can lower creatinine production as proteins break down into creatinine.
- Medications: Prescribed drugs to manage underlying conditions, such as hypertension or diabetes, can help reduce creatinine levels.
- Dialysis: In severe cases, dialysis may be necessary to remove waste products, including creatinine, from the blood.
- Lifestyle Modifications: Regular exercise, avoiding nephrotoxic drugs, and maintaining a healthy weight can support kidney health and lower creatinine levels.
GFR with Creatinine of 2.7
When discussing kidney function, it’s essential to understand the concept of Glomerular Filtration Rate (GFR). GFR is a measure of how well your kidneys are filtering blood, providing a more comprehensive picture of kidney health compared to just the creatinine levels alone. While a creatinine level of 2.7 can be concerning, it’s the GFR that offers a clearer indication of kidney performance. This is because GFR accounts for various factors such as age, sex, and body size, making it a more accurate reflection of kidney function. Therefore, while an elevated creatinine level can signal a potential issue, GFR is the more relevant metric in determining the severity and progression of kidney disease.
| GFR Grade | GFR Range (mL/min/1.73 m²) | Description | Implications |
|---|---|---|---|
| G1 | ≥ 90 | Normal or High | Kidney function is normal, no significant issues. |
| G2 | 60-89 | Mildly Decreased | Minor kidney damage, but function is generally acceptable. Regular monitoring recommended. |
| G3a | 45-59 | Mild to Moderate Decrease | Some loss of kidney function. May require lifestyle changes and monitoring. |
| G3b | 30-44 | Moderate to Severe Decrease | Significant reduction in kidney function. Medical intervention might be necessary. |
| G4 | 15-29 | Severely Decreased | Severe kidney damage. Likely needs medical treatment and preparation for dialysis or transplant. |
| G5 | < 15 | Kidney Failure | Kidneys are no longer functioning adequately. Requires dialysis or a kidney transplant. |
What is my GFR for a creatinine of 2.7
| Age | Gender | GFR |
|---|---|---|
| 18 | male | 30.93 ml/m2 |
| 45 | male | 25.68 ml/m2 |
| 60 | male | 24.23 ml/m2 |
| 80 | male | 22.85 ml/m2 |
| 18 | female | 22.95 ml/m2 |
| 45 | female | 19.06 ml/m2 |
| 60 | female | 17.98 ml/m2 |
| 80 | female | 16.96 ml/m2 |
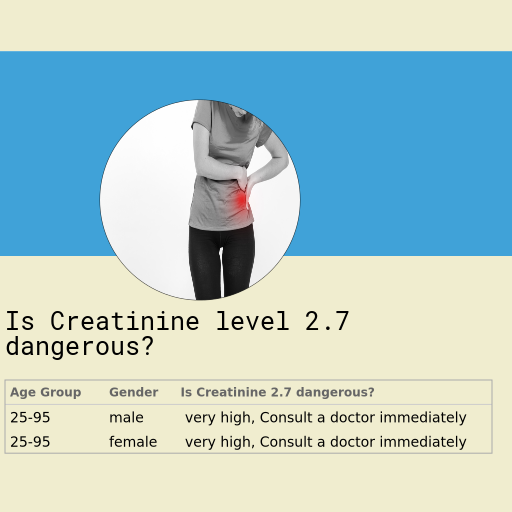
Table of danger posed by Creatinine 2.7 in male across different ages
| Age Group | Is Creatinne of 2.7 dangerous? |
|---|---|
| 25yrs - 95 yrs | very high, Consult a doctor immediately |
Table of danger posed by Creatinine 2.7 in female across different ages
| Age Group | Is Creatinne of 2.7 dangerous? |
|---|---|
| 25yrs - 95 yrs | very high, Consult a doctor immediately |
Which other tests should be done for a creatinine value of 2.7?
In addition to monitoring creatinine levels, it's crucial to consider other diagnostic tests that provide a comprehensive understanding of kidney health. Electrolytes tests measure the levels of essential minerals like sodium, potassium, and chloride, which are vital for various bodily functions. The renal profile offers a more detailed examination of kidney function, often including blood urea nitrogen (BUN) and glomerular filtration rate (GFR). Additionally, blood gas levels are important as they reveal information about oxygen, carbon dioxide, and the pH of your blood, helping to identify any acid-base imbalances. Together, these tests offer a well-rounded view of your renal health and can aid in diagnosing underlying issues that may need attention.
- Electrolytes: This test measures the levels of essential minerals in the blood, such as sodium, potassium, and chloride. Abnormal levels may indicate kidney dysfunction or other medical conditions.
- Renal Profile: A comprehensive renal profile includes tests like serum creatinine, blood urea nitrogen (BUN), and estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) to assess overall kidney function.
- Blood Gas Levels: This test evaluates the levels of oxygen and carbon dioxide in the blood, as well as the blood's pH. It helps in assessing respiratory function and metabolic status, particularly in patients with kidney disease.
- HbA1c: Hemoglobin A1c measures the average blood sugar levels over the past 2-3 months. It's crucial for diagnosing and monitoring diabetes, which can have a direct impact on kidney health.
- Liver Enzymes: Tests like ALT, AST, and ALP measure enzyme levels produced by the liver. Elevated levels can indicate liver disease, which can also affect kidney function.

 By: Dr.Bhargav Raut
By: Dr.Bhargav Raut